目录
滑动窗口是用来做什么的
可以使用滑动窗口进行速率限制。比如TCP的滑动窗口机制:http://timd.cn/tcp-window/。
使用滑动窗口限速的好处是其比较平滑。
什么是滑动窗口
滑动窗口用来“框住”一段连续的元素序列。比如,一个时间序列,或一个环行缓冲区的子序列等。滑动窗口具有左右两个边缘,并且每个边缘都可以左移或右移。比如时间或环行缓冲区,可以被认为是向右无限延伸的,因此左边缘左移一般是一种不合规的行为。
如何实现滑动窗口
下面看hystrix中是如何实现的:
在hystrix中,一个滑动窗口,包含若干个桶(默认是10个),每个桶保存一定时间间隔内的统计数据(默认是1s)。下面看一个官方的例子:
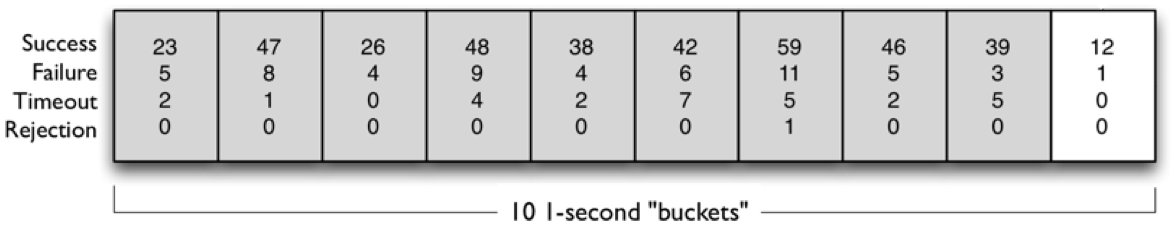
上图中,每个矩形框代表一个桶,每个桶记录着1秒内的4个指标数据:成功量、失败量、超时量、拒绝量。这10个桶合起来就是一个完整的滑动窗口。
从业务上讲,值得注意的是:桶对象有一个不可变的属性-windowStart,它表明该桶对象用来保存[windowStart, windowStart + bucketSizeInMillseconds)时间段内的统计信息。
从技术来讲,值得注意的是:因为每个桶都会被多个线程并发地更新指标数据,所以桶对象需要提供一些线程安全的数据结构和更新方法。为此,hystrix大量使用了CAS,而不是锁。
hystrix使用一个环形数组来维护这些桶,并且它的环形数组的实现类似于一个FIFO的队列。该数组实现有一个叫addLast(Bucket o)的方法,用于向环形数组的末尾追加新的桶对象,当数组中的元素个数没超过最大大小时,只是简单的维护尾指针;否则,在维护尾指针时,还要通过维护首指针,将第一个位置上元素剔除掉。可以看出,该环形数组的表现类似于FIFO队列。
更新统计数据时,都是向当前最新的bucket中更新的,因此hystrix的滑动窗口类HystrixRollingNumber中提供了getCurrentBucket()方法,获取当前最新的bucket。其执行流程如下:
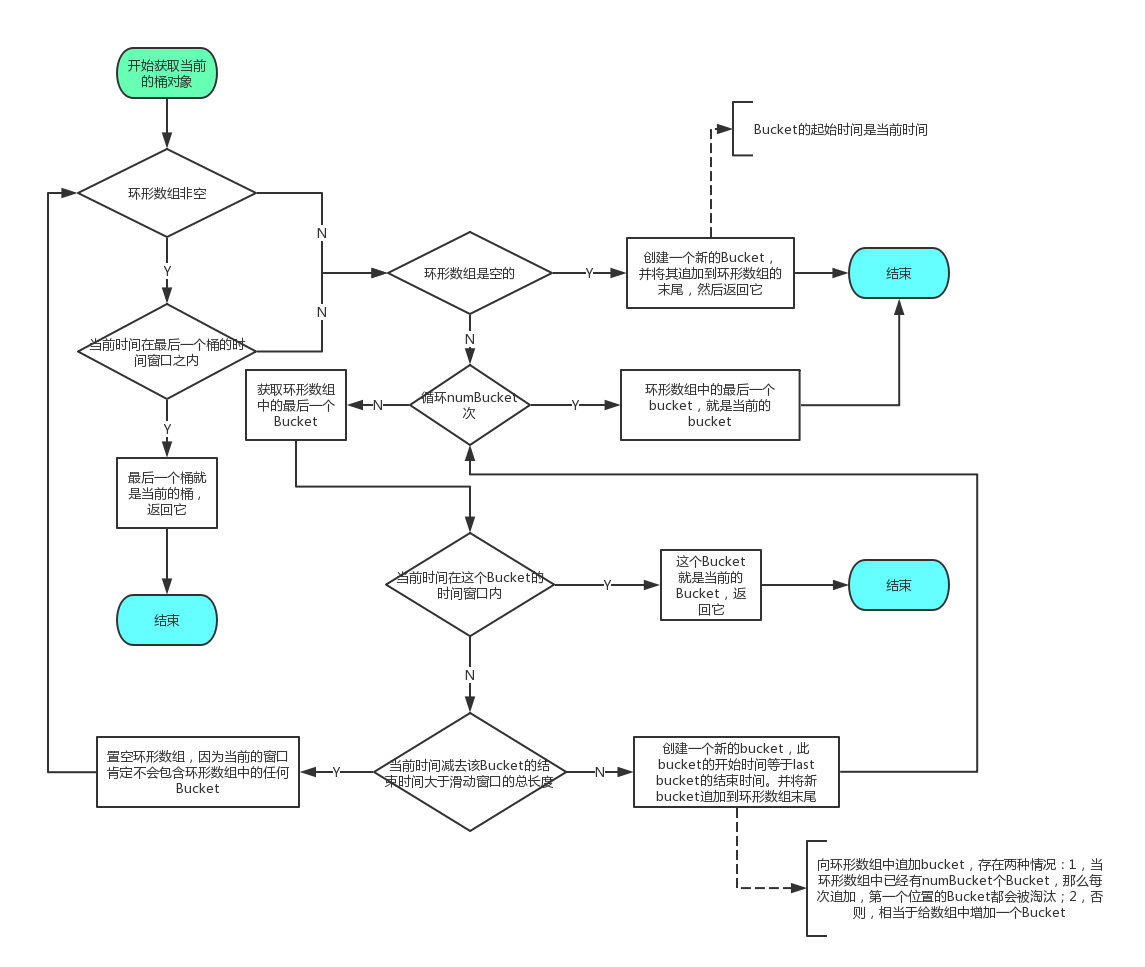
可以看出:滑动窗口每次只向前滑动一个bucket,因此非常的平滑。
如果想要了解hystrix,请自行查阅资料,参考文档中有hystrix的滑动窗口类HystrixRollingNumber的实现。
滚动窗口和滑动窗口
通俗点讲,滑动窗口是向前滑的,而滚动窗口是向前滚的。滑动窗口每次向前滑的距离可以小于窗口的长度,假设有两个相邻的时刻t1、t2,t1时刻的滑动窗口和t2时刻的滑动窗口是可以有交叉的。而滚动窗口向前滚的距离至少是窗口的长度,因此 ,两个相邻时刻的滚动窗口,不会有交叉。
相比之下,滚动窗口没有滑动窗口那么平滑,因为:滑动窗口会继承前一个窗口的部分信息,而滚动窗口不会继承前一个窗口的任何信息。下面是博主基于滚动窗口实现的熔断器:
x
import threadingfrom typing import Optional
class WindowStatus: """ 窗口状态: 开放 半开 关闭 """ OPEN: int = 0x1 HALF_OPEN: int = 0x10 CLOSED: int = 0x100
class Window: """ 窗口对象,其中包含: 起始位置 窗口长度 窗口状态 窗口期内的总请求数 窗口期内的失败请求数 """
def __init__(self, start_position: float, status: int, open_length: float, closed_length: float, half_open_length: float, failure_ratio_threshold: float, failure_count_threshold: float, half_failure_count_threshold: float) -> None: """ :param start_position: 起始位置 :param status: 状态 :param open_length: 开放状态的窗口长度 :param closed_length: 关闭状态的窗口长度 :param half_open_length: 半开状态的窗口长度 :param failure_ratio_threshold: 失败比例阈值 :param failure_count_threshold: 失败数量阈值 :param half_failure_count_threshold: 半失败数量阈值 """ self._start_position: float = start_position self._status: int = status self._open_length: float = open_length self._closed_length: float = closed_length self._half_open_length: float = half_open_length self._failure_ratio_threshold: float = failure_ratio_threshold self._failure_count_threshold: float = failure_count_threshold self._half_failure_count_threshold: float = half_failure_count_threshold
self._lock = threading.RLock() # 统计信息 self._total_count: int = 0 self._failure_count: int = 0
def _fetch(self, position: float) -> Optional[int]: """ 使用指定的位置"推动"窗口前进 :param position: 位置 :return: 窗口的状态 nbsp; """ with self._lock: # 位置在窗口左边缘的左侧时,忽略它 if position < self._start_position: return # 位置在窗口右边缘的右侧时,分以下情况: if position > self._get_end_position(): # 1,如果窗口是半开或打开的,直接右移 if self._status & WindowStatus.HALF_OPEN or self._status & WindowStatus.OPEN: self._enter_into_open_status(position) return self._status # 2,如果当前窗口是关闭的,先进入到下一阶段的半开状态,然后递归处理 elif self._status & WindowStatus.CLOSED: self._enter_into_half_open_status(self._get_end_position()) return self._fetch(position) # 位置在窗口内时,直接返回 else: return self._status
def _get_end_position(self) -> float: """ 获取窗口的结束位置 :return: 窗口的结束位置 """ if self._status & WindowStatus.OPEN: return self._start_position + self._open_length elif self._status & WindowStatus.CLOSED: return self._start_position + self._closed_length else: return self._start_position + self._half_open_length
def get_status(self, position: float) -> int: """ 使用指定的位置获取窗口的状态 :param position: 位置 :return: 窗口的状态 """ return self._fetch(position)
def update_status(self, position: float, success_count: int, failure_count: int) -> None: """ 更新窗口状态 :param position: 位置 :param success_count: 成功请求数 :param failure_count: 失败请求数 """ with self._lock: # 推进窗口 status: int = self._fetch(position) if status is None: return # 当窗口处于关闭状态时,不允许更新窗口的统计 if status & WindowStatus.CLOSED: return # 更新统计信息 if success_count > 0: self._total_count = self._total_count + success_count if failure_count > 0: self._total_count = self._total_count + failure_count self._failure_count = self._failure_count + failure_count
if self._total_count == 0: current_failure_ratio: float = 0 else: current_failure_ratio: float = self._failure_count / (self._total_count + 0.)
# 当失败率达到阈值的时候,窗口进入到 CLOSED 状态 if status == WindowStatus.OPEN: if current_failure_ratio >= self._failure_ratio_threshold: if self._failure_count_threshold is None or \ self._failure_count >= self._failure_count_threshold: self._enter_into_close_status(position) return if status == WindowStatus.HALF_OPEN: if current_failure_ratio >= self._failure_ratio_threshold: if self._half_failure_count_threshold is None or \ self._failure_count >= self._half_failure_count_threshold: self._enter_into_close_status(position) return def _reset_counts(self) -> None: """ 重置统计数据 """ self._failure_count = 0 self._total_count = 0
def _enter_into_close_status(self, position: float) -> None: """ 进入关闭状态 :param position: 窗口的起始位置 """ self._start_position = position self._status = WindowStatus.CLOSED self._reset_counts()
def _enter_into_open_status(self, position: float) -> None: """ 进入打开状态 :param position: 窗口的起始位置 """ self._start_position = position self._status = WindowStatus.OPEN self._reset_counts()
def _enter_into_half_open_status(self, position: float) -> None: """ 进入半开状态 :param position: 窗口的起始位置 """ self._start_position = position self._status = WindowStatus.HALF_OPEN self._reset_counts()
def get_failure_count(self) -> int: """ 获取失败的请求数 :return: 失败的请求数 """ return self._failure_count
def get_success_count(self) -> int: """ 获取成功的请求数 :return: 成功的请求数 """ return self._total_count - self._failure_count