概述
本文将通过源代码对 Redis 的 zset(sorted set)的实现原理进行分析。
Redis 源码
Redis 源码在:https://github.com/redis/redis。
README. md
xxxxxxxxxx...Inside server.c you can find code that handles other vital things of the Redis server:* ...* ...* ...* The global variable `redisCommandTable` defines all the Redis commands, specifying the name of the command, the function implementing the command, the number of arguments required, and other properties of each command....src/server.c 源文件中定义的全局变量 redisCommandTable 用于定义所有 Redis 命令,指定命令的名称、实现命令的函数、命令需要的参数的个数、命令的其它属性。
src/server.c
x
struct redisCommand redisCommandTable[] = { {"zadd",zaddCommand,-4, "write use-memory fast @sortedset", 0,NULL,1,1,1,0,0,0},};接下来都将以 zadd 命令为例进行说明,zadd 命令的实现函数是 zaddCommand(),它的声明在 src/server.h 头文件中:
x
/* Compact list data structure *//* Sorted set object. *//* Raw representation *//* Encoded as ziplist *//* Encoded as skiplist */typedef struct redisObject { unsigned type:4; unsigned encoding:4; unsigned lru:LRU_BITS; /* LRU time (relative to global lru_clock) or * LFU data (least significant 8 bits frequency * and most significant 16 bits access time). */ int refcount; void *ptr;} robj;typedef struct zset { dict *dict; zskiplist *zsl;} zset;robj *createObject(int type, void *ptr);robj *createZsetObject(void);robj *createZsetZiplistObject(void);void zaddCommand(client *c);src/Makefile
如果对 Makefile 不了解,可以先阅读:http://timd.cn/makefile/
x
REDIS_SERVER_NAME=redis-server$(PROG_SUFFIX)REDIS_SERVER_OBJ=... object.o t_zset.o ...all: $(REDIS_SERVER_NAME) ...# redis-server$(REDIS_SERVER_NAME): $(REDIS_SERVER_OBJ) $(REDIS_LD) -o $@ $^ ../deps/hiredis/libhiredis.a ../deps/lua/src/liblua.a $(FINAL_LIBS)%.o: %.c .make-prerequisites $(REDIS_CC) -MMD -o $@ -c $<通过 Makefile 可以看出与 zset 相关的命令由 src/t_zset.c 源文件中定义的函数实现。
src/t_zset.c
x
void zaddGenericCommand(client *c, int flags) { /* 该循环退出后,scoreidx 被设置为第一个 score-element 对的 score 部分在参数列表中的索引 */ /* Parse options. At the end 'scoreidx' is set to the argument position * of the score of the first score-element pair. */ scoreidx = 2; while(scoreidx < c->argc) { scoreidx++; } /* 从 db 中查找 sorted set */ zobj = lookupKeyWrite(c->db,key); /* 如果 sorted set 不存在,则创建它 */ if (zobj == NULL) { /* 如果 zset_max_ziplist_entries 选项被设置为 0,或 * 第一个元素的长度大于 zset_max_ziplist_value 选项, * 则创建使用 Skiplist 编码的 sorted set; * 否则,创建使用 Ziplist 编码的 sorted set */ if (server.zset_max_ziplist_entries == 0 || server.zset_max_ziplist_value < sdslen(c->argv[scoreidx+1]->ptr)) { zobj = createZsetObject(); } else { zobj = createZsetZiplistObject(); } /* 将新创建的 sorted set 即 zobj 对象添加到数据库中 */ dbAdd(c->db,key,zobj); } /* 调用 zsetAdd 将所有 score-element 对添加到 sorted set 中 */ for (j = 0; j < elements; j++) { double newscore; score = scores[j]; int retflags = flags; ele = c->argv[scoreidx+1+j*2]->ptr; int retval = zsetAdd(zobj, score, ele, &retflags, &newscore); }}/* zaddCommand() 是 zadd 命令的实现函数,它调用 zaddGenericCommand() */void zaddCommand(client *c) { zaddGenericCommand(c,ZADD_NONE);}createZsetObject() 和 createZsetZiplistObject() 的实现在 src/object.c 源文件中:
x
robj *createObject(int type, void *ptr) { robj *o = zmalloc(sizeof(*o)); o->type = type; o->encoding = OBJ_ENCODING_RAW; o->ptr = ptr; o->refcount = 1; /* Set the LRU to the current lruclock (minutes resolution), or * alternatively the LFU counter. */ if (server.maxmemory_policy & MAXMEMORY_FLAG_LFU) { o->lru = (LFUGetTimeInMinutes()<<8) | LFU_INIT_VAL; } else { o->lru = LRU_CLOCK(); } return o;}robj *createZsetObject(void) { zset *zs = zmalloc(sizeof(*zs)); robj *o; zs->dict = dictCreate(&zsetDictType,NULL); zs->zsl = zslCreate(); o = createObject(OBJ_ZSET,zs); o->encoding = OBJ_ENCODING_SKIPLIST; return o;}robj *createZsetZiplistObject(void) { unsigned char *zl = ziplistNew(); robj *o = createObject(OBJ_ZSET,zl); o->encoding = OBJ_ENCODING_ZIPLIST; return o;}可见当使用 Skiplist 编码时,用到了 dict 和 Skiplist;当使用 Ziplist 编码时,用到了 Ziplist。后面将对 Skiplist 和 Ziplist 进行分析。
接下来看 zsetAdd() 的流程:
x
int zsetAdd(robj *zobj, double score, sds ele, int *flags, double *newscore) { /* Turn options into simple to check vars. */ int incr = (*flags & ZADD_INCR) != 0; int nx = (*flags & ZADD_NX) != 0; int xx = (*flags & ZADD_XX) != 0; int gt = (*flags & ZADD_GT) != 0; int lt = (*flags & ZADD_LT) != 0; *flags = 0; /* We'll return our response flags. */ double curscore; /* NaN as input is an error regardless of all the other parameters. */ if (isnan(score)) { *flags = ZADD_NAN; return 0; } /* 根据 sorted set 的编码更新它 */ /* Update the sorted set according to its encoding. */ if (zobj->encoding == OBJ_ENCODING_ZIPLIST) { /* 下面是 Ziplist 编码的 sorted set 的更新流程 */ /* if 语句块中是元素已经在 sorted set 中的情况 */ if ((eptr = zzlFind(zobj->ptr,ele,&curscore)) != NULL) { /* 如果设置了 nx 标记,则返回,因为相同的元素已经存在 */ /* NX? Return, same element already exists. */ if (nx) { *flags |= ZADD_NOP; return 1; } /* 如果设置了 incr 标记,那么计算新 score */ /* Prepare the score for the increment if needed. */ if (incr) { score += curscore; if (isnan(score)) { *flags |= ZADD_NAN; return 0; } if (newscore) *newscore = score; } /* 当 score 有变动时,移除、重新插入元素 */ /* Remove and re-insert when score changed. */ if (score != curscore && /* LT? Only update if score is less than current. */ (!lt || score < curscore) && /* GT? Only update if score is greater than current. */ (!gt || score > curscore)) { zobj->ptr = zzlDelete(zobj->ptr,eptr); zobj->ptr = zzlInsert(zobj->ptr,ele,score); *flags |= ZADD_UPDATED; } return 1; /* 更新已存在的元素的分值时,Ziplist 的长度不会发生改变, * 所以不会触发转换成 SkipList 的操作 */ /* 如果元素不存在,且未设置 xx 标记,则插入元素 */ } else if (!xx) { /* 将元素和 score 插入到 Ziplist */ /* Optimize: check if the element is too large or the list * becomes too long *before* executing zzlInsert. */ zobj->ptr = zzlInsert(zobj->ptr,ele,score); /* 如果 Ziplist 中的元素数超过 zset_max_ziplist_entries 选项, * 或新插入的元素的长度超过 zset_max_ziplist_value 选项, * 则将 sorted set 转换成 SkipList 编码 */ if (zzlLength(zobj->ptr) > server.zset_max_ziplist_entries || sdslen(ele) > server.zset_max_ziplist_value) zsetConvert(zobj,OBJ_ENCODING_SKIPLIST); if (newscore) *newscore = score; *flags |= ZADD_ADDED; return 1; /* 否则,直接返回 */ } else { *flags |= ZADD_NOP; return 1; } } else if (zobj->encoding == OBJ_ENCODING_SKIPLIST) { zset *zs = zobj->ptr; zskiplistNode *znode; dictEntry *de; /* 通过哈希表判断元素是否已经在 sorted set 中 */ de = dictFind(zs->dict,ele); /* 下面是元素已经在 sorted set 中的情况,与使用 Ziplist 编码的情况类似 */ if (de != NULL) { /* NX? Return, same element already exists. */ if (nx) { *flags |= ZADD_NOP; return 1; } curscore = *(double*)dictGetVal(de); /* Prepare the score for the increment if needed. */ if (incr) { score += curscore; if (isnan(score)) { *flags |= ZADD_NAN; return 0; } if (newscore) *newscore = score; } /* Remove and re-insert when score changes. */ if (score != curscore && /* LT? Only update if score is less than current. */ (!lt || score < curscore) && /* GT? Only update if score is greater than current. */ (!gt || score > curscore)) { znode = zslUpdateScore(zs->zsl,curscore,ele,score); /* Note that we did not removed the original element from * the hash table representing the sorted set, so we just * update the score. */ dictGetVal(de) = &znode->score; /* Update score ptr. */ *flags |= ZADD_UPDATED; } return 1; } else if (!xx) { /* 复制元素 */ ele = sdsdup(ele); /* 将 score-ele 对插入到跳表中 */ znode = zslInsert(zs->zsl,score,ele); /* 将 ele 和 score 之间的映射关系保存到哈希表中 */ serverAssert(dictAdd(zs->dict,ele,&znode->score) == DICT_OK); *flags |= ZADD_ADDED; if (newscore) *newscore = score; return 1; } else { *flags |= ZADD_NOP; return 1; } } else { serverPanic("Unknown sorted set encoding"); } return 0; /* Never reached. */}综上得出:
sorted set 的编码可以是 Skiplist,也可以是 Ziplist。并且只有当下面的两个条件都满足时,才会使用 Ziplist 编码:
- 元素数量不超过 zset_max_ziplist_entries 选项
- 所有元素的长度都不超过 zset_max_ziplist_value 选项
如果 sorted set 的编码是 Ziplist,并且新插入的元素导致上面的两个条件不再同时满足,那么 Redis 会将其编码转换成 SkipList。
Skiplist 源码解析
如果对跳表不了解,可以先阅读:http://timd.cn/data-structure/skiplist/
以下是 src/server.h 中定义的两个结构体:
xxxxxxxxxx/* Dynamic safe strings *//* ZSETs use a specialized version of Skiplists */typedef struct zskiplistNode { sds ele; double score; struct zskiplistNode *backward; struct zskiplistLevel { struct zskiplistNode *forward; unsigned long span; } level[];} zskiplistNode;typedef struct zskiplist { struct zskiplistNode *header, *tail; unsigned long length; int level;} zskiplist;其中:
zskiplistNode 是跳表的节点:
ele 表示跳表中的元素
score 表示元素的分值,跳表根据该值对节点进行排序
backward 指向前一个节点,头节点和第一节点的前一个节点是 NULL
数组 level:
level 的长度表示节点占据的高度,头节点的高度是 ZSKIPLIST_MAXLEVEL,其它节点的高度在 1 和 ZSKIPLIST_MAXLEVEL 之间(包含 1 和 ZSKIPLIST_MAXLEVEL)
分量 level[i] 包含 2 个域:
- forward 指向第 i 层上的下一个节点,最后一个节点在第 i 层上的下一个节点是 NULL
- span 表示到第 i 层的下一个节点之间的节点数量
zskiplist 是跳表:
- header、tail 分别指向跳表的头节点、尾节点
- length 表示跳表的长度
- level 表示跳表当前的最大层数
下面是一个Redis SkipList 的示例(未画 backward 指针):
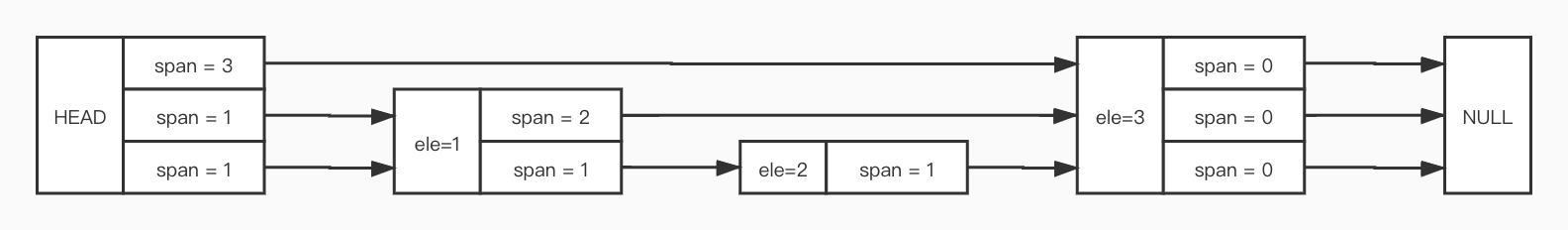
下面分析几个与跳表有关的操作:
1,创建跳表:
xxxxxxxxxx/* Create a skiplist node with the specified number of levels. * The SDS string 'ele' is referenced by the node after the call. */zskiplistNode *zslCreateNode(int level, double score, sds ele) { zskiplistNode *zn = zmalloc(sizeof(*zn)+level*sizeof(struct zskiplistLevel)); zn->score = score; zn->ele = ele; return zn;}/* Create a new skiplist. */zskiplist *zslCreate(void) { int j; zskiplist *zsl; zsl = zmalloc(sizeof(*zsl)); zsl->level = 1; zsl->length = 0; /* 创建头节点,并对其初始化 */ zsl->header = zslCreateNode(ZSKIPLIST_MAXLEVEL,0,NULL); for (j = 0; j < ZSKIPLIST_MAXLEVEL; j++) { zsl->header->level[j].forward = NULL; zsl->header->level[j].span = 0; } zsl->header->backward = NULL; zsl->tail = NULL; return zsl;}其中:
- zslCreateNode() 用于使用指定的层数创建跳表节点
- zslCreate() 用于创建新跳表
2,向跳表中插入新节点:
xxxxxxxxxx/* Returns a random level for the new skiplist node we are going to create. * The return value of this function is between 1 and ZSKIPLIST_MAXLEVEL * (both inclusive), with a powerlaw-alike distribution where higher * levels are less likely to be returned. */int zslRandomLevel(void) { int level = 1; while ((random()&0xFFFF) < (ZSKIPLIST_P * 0xFFFF)) level += 1; return (level<ZSKIPLIST_MAXLEVEL) ? level : ZSKIPLIST_MAXLEVEL;}/* Insert a new node in the skiplist. Assumes the element does not already * exist (up to the caller to enforce that). The skiplist takes ownership * of the passed SDS string 'ele'. */zskiplistNode *zslInsert(zskiplist *zsl, double score, sds ele) { zskiplistNode *update[ZSKIPLIST_MAXLEVEL], *x; unsigned int rank[ZSKIPLIST_MAXLEVEL]; int i, level; serverAssert(!isnan(score)); x = zsl->header; for (i = zsl->level-1; i >= 0; i--) { /* store rank that is crossed to reach the insert position */ rank[i] = i == (zsl->level-1) ? 0 : rank[i+1]; while (x->level[i].forward && (x->level[i].forward->score < score || (x->level[i].forward->score == score && sdscmp(x->level[i].forward->ele,ele) < 0))) { rank[i] += x->level[i].span; x = x->level[i].forward; } update[i] = x; } /* Redis 的 Skiplist 允许不同元素具有相同的分值,并且可以保证不会重复插入相同的元素, * 因为 zslInsert() 的调用方应该在插入元素之前检测其是否在哈希表中。 */ /* we assume the element is not already inside, since we allow duplicated * scores, reinserting the same element should never happen since the * caller of zslInsert() should test in the hash table if the element is * already inside or not. */ level = zslRandomLevel(); if (level > zsl->level) { for (i = zsl->level; i < level; i++) { rank[i] = 0; update[i] = zsl->header; update[i]->level[i].span = zsl->length; } zsl->level = level; } x = zslCreateNode(level,score,ele); for (i = 0; i < level; i++) { x->level[i].forward = update[i]->level[i].forward; update[i]->level[i].forward = x; /* update span covered by update[i] as x is inserted here */ x->level[i].span = update[i]->level[i].span - (rank[0] - rank[i]); update[i]->level[i].span = (rank[0] - rank[i]) + 1; } /* increment span for untouched levels */ for (i = level; i < zsl->level; i++) { update[i]->level[i].span++; } x->backward = (update[0] == zsl->header) ? NULL : update[0]; if (x->level[0].forward) x->level[0].forward->backward = x; else zsl->tail = x; zsl->length++; return x;}其中:
- zslRandomLevel() 的返回值是 1 和 ZSKIPLIST_MAXLEVEL 之间的一个整数(包含 1 和 ZSKIPLIST_MAXLEVEL)
- zslInsert() 用于向跳表中插入新节点
下面对 zslInsert() 的代码进行分析:
从最高层向下,逐层寻找每层的插入位置,并计算插入位置到头节点的距离
- update[] 数组中的第 i 个分量表示:在第 i 层,新节点将被插入到 update[i] 的后面
- rank[] 数组中的第 i 个分量表示:update[i] 距离头节点的长度
随机生成新节点占据的层数 level(1 到 ZSKIPLIST_MAXLEVEL 之间)
如果 level 大于跳表的当前高度,那么更新 update[]、rank[],重置跳表的高度
创建新节点 x
从最底层向上,调整插入点和新节点的 forward 指针,以及 span 值,直到 level
递增未达到的层级的 span 值
调整 x 以及 x 的 forward 的 backward 指针;如果 x 是最后一个节点,将跳表的 tail 指向它
增加跳表长度
关于查找、删除等操作,以后有机会再补充。通过这两个函数已经可以对 Redis Skiplist 有完整的了解了。
Ziplist 介绍
Ziplist 的源码在 src/ziplist.c 源文件中。
1,Ziplist 的总体布局
<zlbytes> <zltail> <zllen> <entry> <entry> ... <entry> <zlend>
注意:除非另外规定,否则所有域都以小端(little endian)格式存储。
<uint32_t zlbytes> 是用于保存 Ziplist 占用的字节数的无符号整数(包含 zlbytes 域本身的四个字节)。存储该值的目的是为了能够在不遍历 Ziplist 的情况下,改变整个结构的大小。
<uint32_t zltail> 是 Ziplist 中最后一个 entry 的偏移。它允许在不遍历整个列表的情况下,在远端执行弹出操作。
<uint32_t zllen> 是entry 的数量。当 entry 的数量超过 2^16-2 时,该值被设置为 2^16-1,此时如果想要知道列表中有多少条目,需要遍历整个列表。
<uint32_t zlend> 是代表 Ziplist 的结尾的特殊 entry。它被编码为等于 255 的单字节。任何常规 entry 的首字节都不会被设置为 255。
2,Ziplist Entry
Ziplist 中的 entry 以包含 2 部分信息的元数据开头:
- 前一个 entry 的长度。存储它的目的是为了支持从后向前遍历列表
- entry 的编码。它表示 entry 的类型:整型或字符串,当 entry 是字符串时,编码也表示字符串的长度
因此,完整的 entry 的结构如下:
<prevlen> <encoding> <entry-data>
有时编码也代表 entry 本身。此时,可以省略 <entry-data> 部分:
<prevlen> <encoding>
前一个 entry 的长度 <prevlen> 的编码方式如下:
- 如果该长度小于 254 字节,它只使用一个字节(8 位无符号整数)表示该长度
- 当该长度大于或等于 254 时,它将占用 5 个字节。第一个字节被设置为 254(FE),这意味着后面是一个较大的值。其余 4 个字节保存前一个 entry 的长度
因此几乎所有 entry 的编码都如下:
<prevlen from 0 to 253> <encoding> <entry-data>
如果前一个 entry 的长度大于 253 字节,那么将使用如下的编码:
0xFE <4 bytes unsigned little endian prevlen> <encoding> <entry-data>
entry 的编码依赖于 entry 的内容:
- 如果 entry 是字符串,编码的第一个字节的前 2 位保存用于存储字符串长度的编码的类型,其后是真正的字符串长度
- 如果 entry 是整型,前 2 位都被设置为 1。后面的 2 位用于指定这个头之后将存储哪种整数
第一个字节足够用于确定 entry 的种类,不同类型和编码的概述如下:
|00pppppp| - 1 字节
长度小于或等于 63 字节(6 位)的字符串值。
"pppppp" 表示 6 位无符号长度
|01pppppp|qqqqqqqq| - 2 字节
长度小于或等于 16383 字节(14 位)的字符串值。
注意:以大端格式存储这个 14 位数值
|10000000|qqqqqqqq|rrrrrrrr|ssssssss|tttttttt| - 5 字节
长度大于或等于 16384 字节的字符串值。
只有第一个字节后面的 4 个字节表示该长度(最大可达 2^32-1)。第一个字节的低 6 位未被使用,且都被设置为 0。
注意:以大端格式存储这个 32位数值
|11000000| - 3 字节
编码为 int16_t(2 字节) 的整数
|11010000| - 5 字节
编码为 int32_t(4 字节) 的整数
|11100000| - 9 字节
编码为 int64_t(8 字节) 的整数
|11110000| - 4 字节
编码为 24 位(3 字节)有符号的整数
|11111110| - 2 字节
编码为 8 位(1 字节)有符号的整数
|1111xxxx| - xxxx 在 0001 和 1101 之间
|11111111| - 代表 Ziplist 结束的特殊 entry
在 Ziplist 头中,所有整数都以小端格式存储。